Pediatirc/ Rickets
Rickets signifies a failure in mineralisation of the growing bone or osteoid tissue. Failure of
mature bone to mineralise is osteomalacia
mature bone to mineralise is osteomalacia
Etiology :
1- vitamin D disorders(nutritional , congenital , secondary, chronic renal failure)
2- calciu m deficiency(diet, malabsorption)
3- phosphorous deficiency( diet, antacid)
4- RENAL LOSSES(X -linked hypophosphatemic rick ets , RTA)
2- calciu m deficiency(diet, malabsorption)
3- phosphorous deficiency( diet, antacid)
4- RENAL LOSSES(X -linked hypophosphatemic rick ets , RTA)
Nutritional Vitamin D Deficiency :
CLINICAL FEATURES OF RICKETS :
GENERAL
Failure to thrive
Listlessness
Protruding abdomen
Muscle weakness (especially proximal)
Fractures
HEAD
Craniotabes (softening of the cranial bon es and can be detected by applying pressure
at the occiput or over the parietal bones. The sensation is similar to the feel of
pressing into a Ping -Pong ball and then releasing)
Frontal bossing
Delayed fontanel closure
Delayed dentition; caries
Craniosynostosis
CHEST
Rachitic rosary
Harrison groove
Respiratory infections and atelectasis*
BACK
Scoliosis
Kyphosis
Lordosis
EXTREMITIES
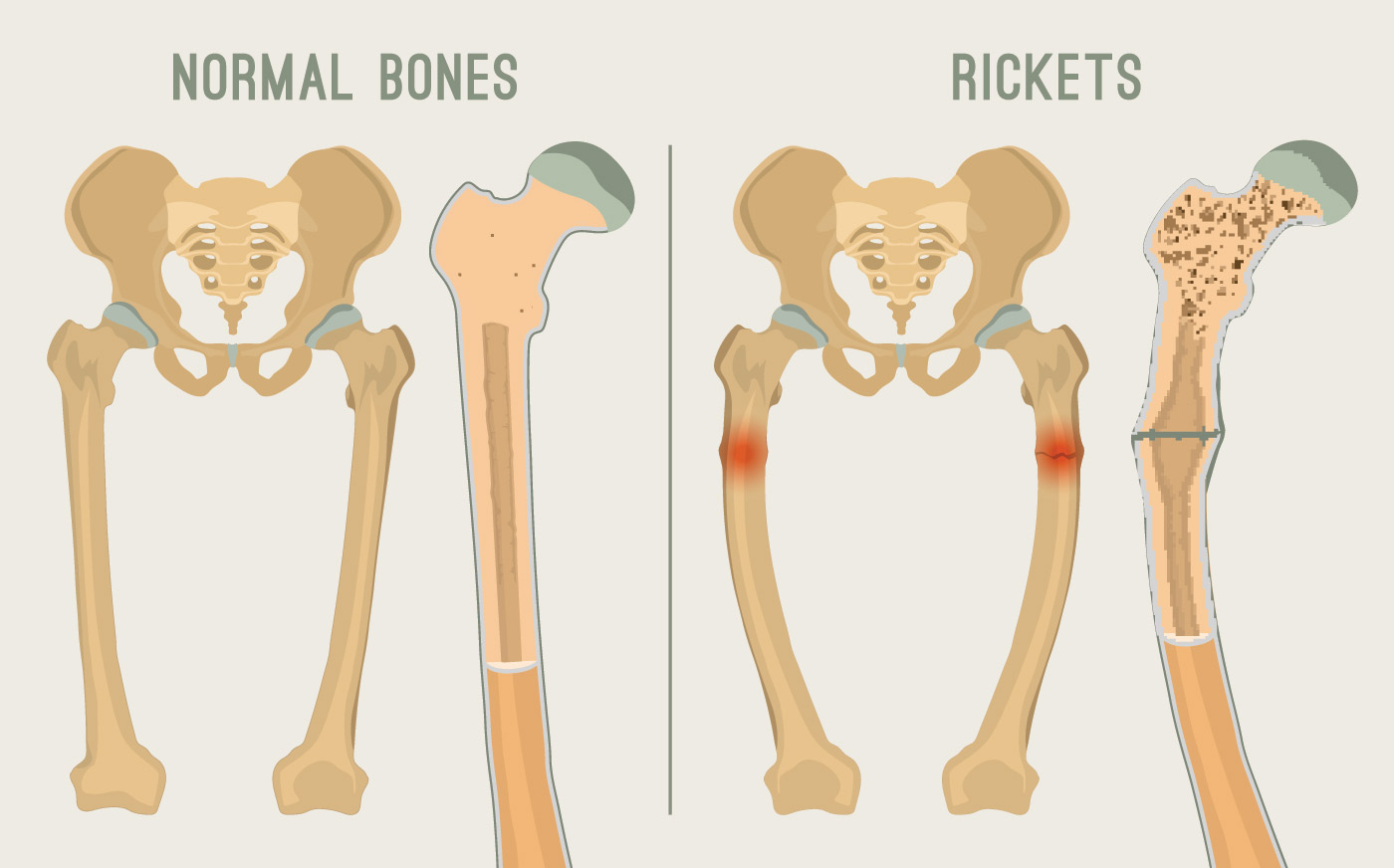
Enlargement of wrists and ankles
Valgus or varus deformities
Windswept deformity (combination of valgus deformity of 1 leg with varus deformity
of the other leg)
Anterior bowing of the tibia and femur
Coxa vara
Leg pain
Failure to thrive
Listlessness
Protruding abdomen
Muscle weakness (especially proximal)
Fractures
HEAD
Craniotabes (softening of the cranial bon es and can be detected by applying pressure
at the occiput or over the parietal bones. The sensation is similar to the feel of
pressing into a Ping -Pong ball and then releasing)
Frontal bossing
Delayed fontanel closure
Delayed dentition; caries
Craniosynostosis
CHEST
Rachitic rosary
Harrison groove
Respiratory infections and atelectasis*
BACK
Scoliosis
Kyphosis
Lordosis
EXTREMITIES
Enlargement of wrists and ankles
Valgus or varus deformities
Windswept deformity (combination of valgus deformity of 1 leg with varus deformity
of the other leg)
Anterior bowing of the tibia and femur
Coxa vara
Leg pain
Most cases of rickets are diagnosed based on the presence of classic radiographic
abnormalities . The diagnosis is supported by physical examination findings and a history
and laboratory test results that are consistent with a specific etiology
and laboratory test results that are consistent with a specific etiology
LABORATORY TESTS
The initial laboratory tests in a child with rickets should include serum calcium, phosphorus,
alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone (PTH), 25 -hydroxyvitamin D, 1,25 -
dihydroxyvitamin D3, creatinine, and electrolytes
alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone (PTH), 25 -hydroxyvitamin D, 1,25 -
dihydroxyvitamin D3, creatinine, and electrolytes
Treatment
Children with nutritional vitamin D deficiency should receive vitamin D and adequate
nutritional intake of calcium and phosphorus. There are 2 strategies for administration of
vitamin D. With stoss therapy, 300,000 -600,000 IU of vitamin D are administered orally or
intramuscularly as 2 -4 doses over 1 day. Because the doses are observed, stoss therapy is
ideal in situations where adherence to therapy is questionable. The alternative is daily,
high -dose vitamin D, with doses ranging from 2,000 -5,000 IU/day over 4 -6 wk . Either
strategy should be followed by daily vitamin D intake of 400 IU/day if <1 yr old or 600
IU/day if >1 yr, typically given as a multivitamin
nutritional intake of calcium and phosphorus. There are 2 strategies for administration of
vitamin D. With stoss therapy, 300,000 -600,000 IU of vitamin D are administered orally or
intramuscularly as 2 -4 doses over 1 day. Because the doses are observed, stoss therapy is
ideal in situations where adherence to therapy is questionable. The alternative is daily,
high -dose vitamin D, with doses ranging from 2,000 -5,000 IU/day over 4 -6 wk . Either
strategy should be followed by daily vitamin D intake of 400 IU/day if <1 yr old or 600
IU/day if >1 yr, typically given as a multivitamin

Comments
Post a Comment