Hyperkalemia
Severe: above 6.5 mmol/l carry
Risk of cardiac stand still in diastole
c/p: progressive muscular weakness or no symptoms
2.Excessive intake (diet, iv therapy..)
3.Redistribution out of cells
4.Endogenous increase K Load
( 5.Medications(ACEI,B-BLOCKER,K-sparingD
: 6.Renal retention of K
(Renal failure or Tubular secretary failure)
Delay in processing of blood
Severe leukocytosis or thrombocytosis
2.Insulin deficiency
3.B-BLOCKERS
4.Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
Rhabdomyolysis
Hemolysis
Tumor lysis syndrome
Severe exercise
A. Sever Acute Renal Failure , esp with Hemolysis , Rhabdomyolysis , Acidosis))
B. Chronic Renal Failure(Advanced)
(esp with oliguria /K load)
2.Congenital adrenal enzyme defect
3. Drugs : ACEIs , B-blockers ,NSAIDs and K Sparing Diuretics..Amiloride,Spironolactone
4.Tubulointerstial disease…no response to the Aldosteron by tubules..(SLE , transplant (,Amyloidosis, Obstructive Uropathy
2- Drive extracellular potassium into the cells
3- Removal of Potassium from the body
2-Soluble Insulin 5-10 u with 25 gm of Glucose(Glucose50ml of 50% concentration) infusion within 10 min :
it will lower K by 0.5-1.5 mmol/L started after 15-30 min ,action remain for several hours.
*infusion of10-20%Dextrose 500ml within4-6hrs to minimize rebound increase in K
3- If Acidosis , IV Sodium Bicarbonate 100ml of 8.4%.
2.Ion Exchange Resin(eg. Calsium Resonium binds K+ in exchange for Ca++) given orally 15-30 g or rectally 30g, which remove K from GIT.
* K-Resin Exchanges Na+ for K+ and binds it in gut, primarily in large intestine, decreasing total body potassium
3.Dialysis if significant renal impairment
Risk of cardiac stand still in diastole
c/p: progressive muscular weakness or no symptoms
Of Hyperkalemia Causes
1.(spurious) Pseudohyperkalemia2.Excessive intake (diet, iv therapy..)
3.Redistribution out of cells
4.Endogenous increase K Load
( 5.Medications(ACEI,B-BLOCKER,K-sparingD
: 6.Renal retention of K
(Renal failure or Tubular secretary failure)
1.Spurious Hyperkalemia
Hemolysis (in tube )Delay in processing of blood
Severe leukocytosis or thrombocytosis
2. Redistribution out of cells
1.Metabolic acidosis2.Insulin deficiency
3.B-BLOCKERS
4.Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
3. Exogenous(diet,K therapy)
4. Endog enous K loadRhabdomyolysis
Hemolysis
Tumor lysis syndrome
Severe exercise
: 5. Renal Retention of K
In renal failure(especially when S.Cr >500 mic mol/L) ie with decrease GFRA. Sever Acute Renal Failure , esp with Hemolysis , Rhabdomyolysis , Acidosis))
B. Chronic Renal Failure(Advanced)
(esp with oliguria /K load)
Conditions with Hyperkalemia due to Renal Tubular Secretary Failure ie with preserved GFR
1.Addison disease2.Congenital adrenal enzyme defect
3. Drugs : ACEIs , B-blockers ,NSAIDs and K Sparing Diuretics..Amiloride,Spironolactone
4.Tubulointerstial disease…no response to the Aldosteron by tubules..(SLE , transplant (,Amyloidosis, Obstructive Uropathy
Investigations
Serum ElectrolytesRenal Function tests (B. urea ,S. Cr ), bicarbonate level
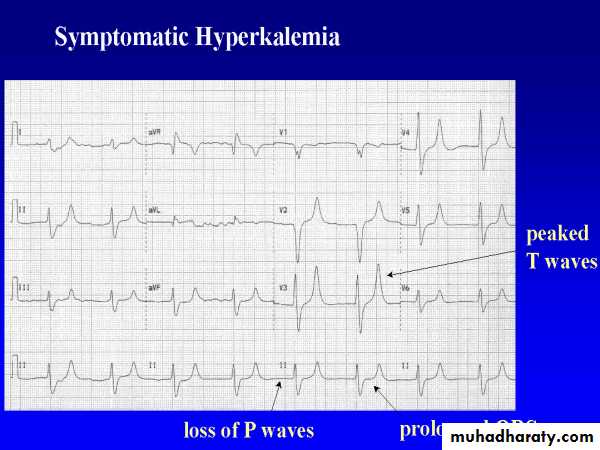
ECGTreatment of Hyperkalemia
1- Stabilize myocardial membrane2- Drive extracellular potassium into the cells
3- Removal of Potassium from the body
Stabilize myocardial cell membrane
Calcium Gluconate 10 ml 10% IV. Over 2-3 min ,repeated if no reversal changes in ECG within 5-10 minDrive extracellular potassium into the cells
1- Inhaled 2 Agonists: or 5-10mg nibulized Salbutamol inhaler over 10 min, it will lower K by 0.5-1.5 mmol/L started after 30 min ,action remain for 2-4 hours.2-Soluble Insulin 5-10 u with 25 gm of Glucose(Glucose50ml of 50% concentration) infusion within 10 min :
it will lower K by 0.5-1.5 mmol/L started after 15-30 min ,action remain for several hours.
*infusion of10-20%Dextrose 500ml within4-6hrs to minimize rebound increase in K
3- If Acidosis , IV Sodium Bicarbonate 100ml of 8.4%.
Removal of Potassium from the body
1.Frusemide IV with Normal Saline if renal function is normal2.Ion Exchange Resin(eg. Calsium Resonium binds K+ in exchange for Ca++) given orally 15-30 g or rectally 30g, which remove K from GIT.
* K-Resin Exchanges Na+ for K+ and binds it in gut, primarily in large intestine, decreasing total body potassium
3.Dialysis if significant renal impairment

Comments
Post a Comment